
Ectopic Pregnancy
- Home
- /
- Gynecological Treatment
- /
- Ectopic Pregnancy
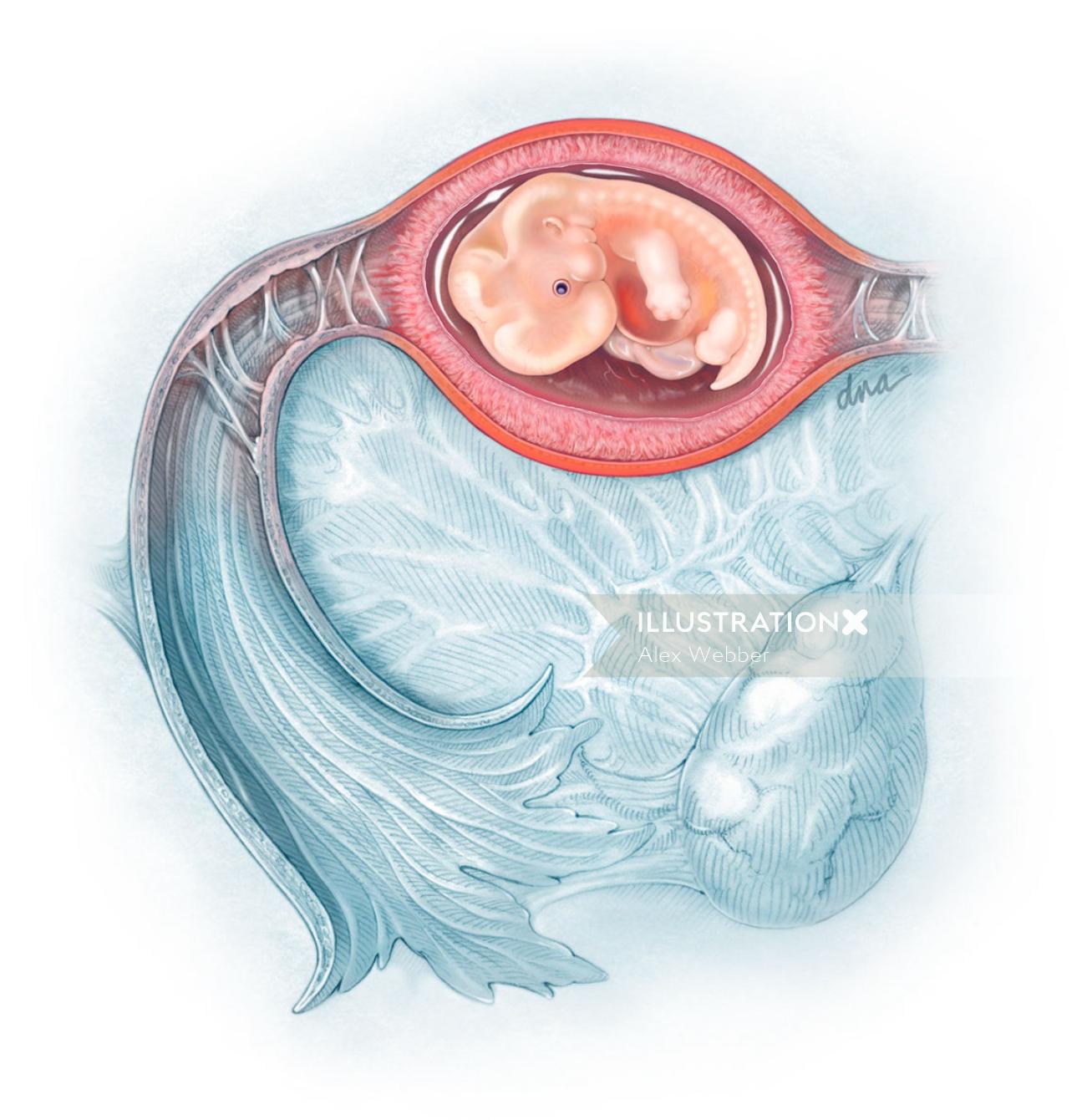
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus, most commonly in a fallopian tube. This can be a life-threatening situation if not promptly diagnosed and treated.
• Abdominal pain, often one-sided
• Vaginal bleeding, which may be lighter than a normal period
• Shoulder pain (less common)
• Dizziness, weakness, or fainting (in severe cases)
The exact cause of an ectopic pregnancy is often unknown, but some factors can increase the risk, such as:
• Previous pelvic surgery
• Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
• Endometriosis
• Smoking
• Using fertility drugs
• Early diagnosis is crucial for timely intervention and better outcomes. Tests used for diagnosis include:
• Pregnancy test
• Pelvic ultrasound
• Blood tests to measure hormone levels.
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy depend on the severity of the situation and the location of the ectopic pregnancy. Options may include:
• Medication: Methotrexate, a medication that can stop the growth of the ectopic pregnancy and allow it to be absorbed by the body, might be used if the pregnancy is very small and there is no bleeding.
• Surgery: Laparoscopy or laparotomy might be needed to remove the ectopic pregnancy if it is larger or causing bleeding.
Ectopic pregnancy can be a life-threatening condition if not treated promptly. Risks include:
• Internal bleeding
• Rupture of the fallopian tube
• Damage to the fallopian tube
• Infertility
• Following treatment, it's important to follow your doctor's instructions for recovery and monitor for any signs of infection or complications. It can take several months for your body to fully recover from an ectopic pregnancy.
• Remember, if you experience any symptoms suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy, seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful recovery and minimize long-term risks.