
Gynaecological Cancer
- Home
- /
- Gynecological Treatment
- /
- Gynecological Cancer
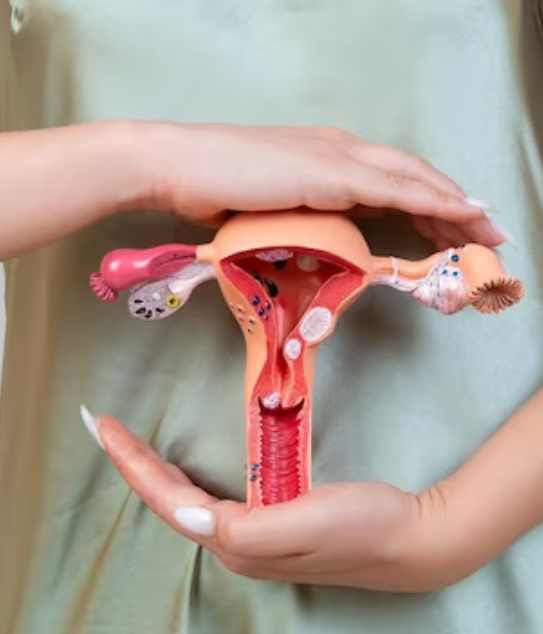
Gynecological cancers are a group of cancers that affect the female reproductive organs. They can be challenging to navigate, but with knowledge and proper care, many women can overcome these challenges and live long, healthy lives.
• Cervical cancer: Arises from the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a major risk factor.
• Ovarian cancer: Starts in the ovaries, which produce eggs and hormones. Early detection is often difficult as symptoms can be vague.
• Uterine cancer: Develops in the lining of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is the most common type, while other types are rarer.
• Vaginal cancer: Affects the vagina, the muscular tube connecting the uterus to the vulva. It's relatively rare compared to other gynecological cancers.
• Vulvar cancer: Starts in the vulva, the external genitalia of women. It can be caused by HPV infection or other factors.
• Age: Risk increases with age for most types of gynecological cancers.
• Family history: Having a family member with a gynecological cancer can increase your risk.
• Genetic factors: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of some types.
• Lifestyle factors: Smoking, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of certain types.
• Sexual history: Multiple sexual partners and a history of sexually transmitted infections can increase the risk of cervical cancer.
Symptoms can vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer, but some common signs include:
• Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge
• Pelvic pain
• Abdominal pain or bloating
• Difficulty urinating or bowel movements
• Weight loss
• Fatigue
Early diagnosis is crucial for successful treatment. Tests used for diagnosis may include:
• Pap test for cervical cancer
• Pelvic exam
• Ultrasound
• Biopsy
Treatment options depend on the type, stage, and other factors of the cancer. Options may include:
• Surgery
• Radiation therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Immunotherapy
• Targeted therapy
• A diagnosis of gynecological cancer can be overwhelming, but there are many resources available to support you. Joining a support group, talking to a therapist, and connecting with other survivors can be helpful.
• Remember, you're not alone. Early detection and proper treatment can significantly improve the chances of successful outcomes for gynecological cancers. If you have any concerns about your health, talk to your doctor.